|

 Up
Up 
 Wright Timeline 1900
to 1909
Wright Timeline 1900
to 1909 
(You
are here.)
 Down
Down




  Need
to Need
to
find your
bearings?
Try
these
navigation aids:
If
this is your first
visit, please stop by:
Something
to share?
Please:



|
|
Available in Française, Español, Português, Deutsch, Россию,
中文,
日本, and others.
 o
invention, no scientific discovery, no work of art, no human
endeavor happens in an historical vacuum. There are always other
factors -- cultural, political, personal -- that influence the
outcome of a single event. So it was with the invention of the
airplane. When Wilbur and Orville were children, the abacus was the most
advanced mathematical aid, influenza was an often-fatal disease, and
the cannon was the most feared weapon of war. By the time Orville
died, the first computers were just being built, antibiotics had
begun to wipe out disease, and the atomic bomb made war
unthinkable. Many of these advances influenced the development of
the airplane -- and the airplane, in turn, influenced further
advances. o
invention, no scientific discovery, no work of art, no human
endeavor happens in an historical vacuum. There are always other
factors -- cultural, political, personal -- that influence the
outcome of a single event. So it was with the invention of the
airplane. When Wilbur and Orville were children, the abacus was the most
advanced mathematical aid, influenza was an often-fatal disease, and
the cannon was the most feared weapon of war. By the time Orville
died, the first computers were just being built, antibiotics had
begun to wipe out disease, and the atomic bomb made war
unthinkable. Many of these advances influenced the development of
the airplane -- and the airplane, in turn, influenced further
advances.
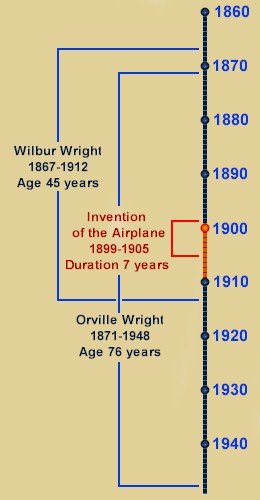
Here is chronology that shows not just the story of the Wright
brothers, but also the world they lived in and the important political,
cultural, and scientific events that loomed large in their lives. Click on the
decade you want to see:
|
 |
Time
|
The Wright
Story
|
The Bigger
Picture
|
|
1900 |
The Wright
brothers fly their first manned glider at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina to test
their control system. It does not produce enough lift to
make more than a handful of flights..
|
 |
Pablo Picasso begins to show his
paintings, Sigmund Freud writes The Interpretation of Dreams, and
Max Planck formulates quantum theory. The US Navy
commissions its first submarine, the USS Holland.
|
 |
|
1901 |
The Wrights test their second glider at Kitty
Hawk. and it also performs poorly. At home in Dayton, Ohio,
they build a wind tunnel and conduct research on wing
shapes.
|
 |
William McKinley is
assassinated; Theodore Roosevelt becomes the US president.
Charles W. Hart and Charles H. Parr introduce a
gasoline-powered farm tractor. |
 |
|
1902 |
The Wright build a third glider based on their wind tunnel
tests and it flies well. They refine their control system at
Kitty Hawk. |
 |
Adolf Miethe
invents the panchromatic process, leading to Autochrome, the first commercially sold color
film. Stanford University and the University of Michigan
play the first college bowl game, the Rose Bowl.
|
 |
|
1903 |
The Wright brothers make
the first controlled, sustained powered flight at Kitty Hawk. Samuel Langley of
the Smithsonian Institution also tries to fly a manned version of his Aerodrome
and fails.
|
 |
The first true
motion picture, The Great Train Robbery, premiers.
It is 12 minutes long. Crayola sells its first box of crayons and the
Pittsburgh Pirates and the Boston Americans play the first
World Series.
|
 |
|
1904 |
The Wrights begin to refine their powered airplane, making
test flights at Huffman Prairie near Dayton, Ohio
|
 |
The first ice cream cones are
sold at the St. Louis World's Fair; a judge in Newark, Rhode
Island pronounces the first jail sentence for speeding in an
automobile. Work on the Panama Canal begins.
|
 |
|
1905 |
The Wright brothers develop the first practical airplane and
demonstrate it before a small audience. They offer their
invention to the U.S. Army, but the Army is not interested.
|
 |
Albert Einstein publishes the Special Theory of
Relativity. The Niagra Movement — later to become the NAACP
— is
founded. The Royal Navy lays the keel of the HMS Dreadnought whose
turbine engines and powerful gun batteries revolutionize naval
warfare.
|
 |
|
1906 |
The U.S. Patent Office grants a patent to the
Wright Brothers on their airplane control system.
|
 |
Reginald Fessenden
makes the first radio broadcast of voice and music from
Massachusetts. Upton Sinclair's
novel The Jungle leads to the U.S. Pure Food and Drug
Act and an earthquake destroys much of San Francisco,
California. Alberto Santos Dumont makes the first powered
flights in Europe.
|
 |
|
1907 |
The Wright Brothers procure contracts for the sale of
airplanes from French investors and the U.S. Army, provided
they can demonstrate their invention.
|
 |
President Theodore Roosevelt speaks to the U.S. Congress
about the "conservation of natural resources," marking
the beginning of the conservation and environmental
movements. Lee DeForest invents the triode, the beginning of
electronics.
|
 |
|
1908 |
The Wright brothers
demonstrate a two-passenger airplane in Europe and America. Orville
crashes during a demonstration flight and is badly injured.
His passenger, Lt. Thomas Selfridge, becomes the first
person to die in an airplane crash.
|
 |
The Ford Motor Company produces the first "Model
T" automobile. Oil is discovered in the Middle East and Lt. General
Robert Baden-Powell writes a book, Scouting for Boys,
that leads to the founding of the Boy Scouts.
|
 |
|
1909 |
The Wrights
demonstrate a new airplane and the U.S. Army buys its first
military aircraft. The Wrights begin to manufacture
airplanes and teach pilots.|
|
 |
Leo Baekeland develops "Bakelight," the first
widely-used plastic, Ernest Rutherford formulates the structure of the
atom, and Richard Peary reaches the north pole. Louis Bleriot flies across
the English Channel in a Bleriot XI.
|
 |
|
|
|
|